
Port forwarding in a Kubernetes cluster is especially useful for back-end services not intended for remote exposure. If a single pod starts failing, you are prepared to access that service and correct any issues. You can now use the port-forward command to connect to any pod within your Kubernetes cluster. The Service selects which pod is to be used: kubectl port-forward service/myservice 8080 5762 Listen and forward data using the same ports (8080 5762) both locally and within the pod. The Deployment defines which pod is to be used: kubectl port-forward deployment/mydeployment 8080 5762 Allow Service to Define port-forward Pod Listen on port 8080 on the localhost using the defined IP, forward to port 5762 in the pod: kubectl port-forward -address localhost,10.153.40.102 pod/mongo-db-r3pl1ka3 8080:5762 Use Deployment to Select port-forward Pod Listen on port 8080 on any local address, forward to port 5762 in the specified pod: kubectl port-forward -address 0.0.0.0 pod/mongo-db-r3pl1ka3 8888:5762 Specify Local IP Address for Port Forwarding Listen and forward data using identical ports (8080, 5762) both locally and within the specific pod: kubectl port-forward pod/mongo-db-r3pl1ka3 8080 5762 Random Local IP Address Listen on a random port locally, and forward to port 5762 within the specified pod: kubectl port-forward pod/mongo-db-r3pl1ka3 :5762 Corresponding Local and Remote Port The Kubernetes API now listens on local port 8080 and forwards data to port 5762 on the defined pod.
Port forwarding automatic windows#
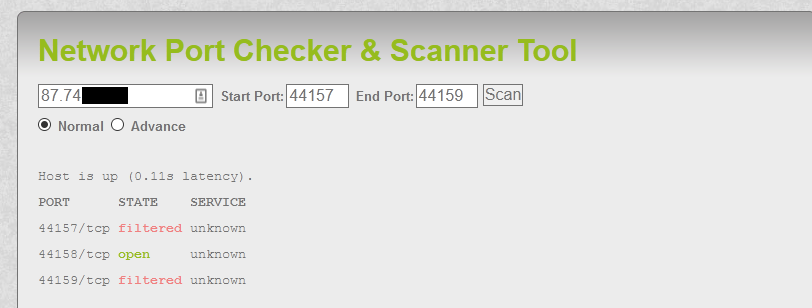
For this tool to work you will need UPnP support on both your Windows OS and network device. This program automatically opens the necessary ports for multiplayer server hosting. The name of the pod is mongo-db-r3pl1ka3, and port number is 5762: kubectl port-forward pod/mongo-db-r3pl1ka3 8080:5762 Setting up ports for multiplayer server hosting is a pain in the ass, so I wrote a program to automate it. However, in some cases, it is the only way to access internal cluster resources.įor instance, the following command would allow you to access a MongoDB deployment within your cluster. Port forwarding is a work-intensive method.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
